Abstract
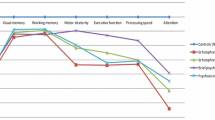
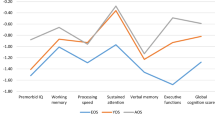
The aims of this study were to examine the nature and extent of cognitive impairment in first-episode early-onset psychosis (FE-EOP) soon after their stabilisation and to search for potential differences according to specific diagnostic sub-groups of patients. As part of a Spanish multicentre longitudinal study, 107 FE-EOP patients and 98 healthy controls were assessed on the following cognitive domains: attention, working memory, executive functioning, and verbal learning and memory. Three diagnostic categories were established in the patient sample: schizophrenia (n = 36), bipolar disorder (n = 19), and other psychosis (n = 52). Patients performed significantly worse than controls in all cognitive domains. The three diagnostic sub-groups did not differ in terms of impaired/preserved cognitive functions or degree of impairment. FE-EOP patients show significant cognitive impairment that, during this early phase, seems to be non-specific to differential diagnosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addington J, Brooks BL, Addington D (2003) Cognitive functioning in first episode psychosis: initial presentation. Schizophr Res 62:59–64
Basso M, Nasrallah H, Olson S, Bornstein R (1997) Cognitive deficits distinguish patients with adolescent- and adult- onset schizophrenia. Neuropsych Neuropsychol Behav Neurol 10:107–112
Bilder RM, Goldman RS, Robinson D, Reiter G, Bell L, Bates JA, Pappadopulos E, Willson DF, Alvir JM, Woerner MG, Geisler S, Kane JM, Lieberman JA (2000) Neuropsychology of first-episode schizophrenia: initial characterization and clinical correlates. Am J Psychiatry 157:549–559
Brickman AM, Buchsbaum MS, Bloom R, Bokhoven P, Paul-Odouard R, Haznedar MM, Dahlman KL, Hazlett EA, Aronowitz J, Heath D, Shihabuddin L (2004) Neuropsychological functioning in first-break, never-medicated adolescents with psychosis. J Nerv Ment Dis 192:615–622
Castro-Fornieles J, Parellada M, Gonzalez-Pinto A, Moreno D, Graell M, Baeza I, Otero S, Soutullo CA, Crespo-Facorro B, Ruiz-Sancho A, Desco M, Rojas-Corrales O, Patino A, Carrasco-Marin E, Arango C (2007) The child and adolescent first-episode psychosis study (CAFEPS): design and baseline results. Schizophr Res 91:226–237
Fagerlund B, Pagsberg AK, Hemmingsen RP (2006) Cognitive deficits and levels of IQ in adolescent onset schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. Schizophr Res 85:30–39
Fitzgerald D, Lucas S, Redoblado MA, Winter V, Brennan J, Anderson J, Harris A (2004) Cognitive functioning in young people with first episode psychosis: relationship to diagnosis and clinical characteristics. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 38:501–510
Fraguas D, de Castro MJ, Medina O, Parellada M, Moreno D, Graell M, Merchan-Naranjo J, Arango C (2008) Does diagnostic classification of early-onset psychosis change over follow-up? Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 39(2):137–145
Gonzalez-Blanch C, Alvarez-Jimenez M, Rodriguez-Sanchez JM, Perez-Iglesias R, Vazquez-Barquero JL, Crespo-Facorro B (2006) Cognitive functioning in the early course of first-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorders: timing and patterns. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256:364–371
Green MF (2006) Cognitive impairment and functional outcome in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 67:e12
Green MF, Nuechterlein KH, Gold JM, Barch DM, Cohen J, Essock S, Fenton WS, Frese F, Goldberg TE, Heaton RK, Keefe RS, Kern RS, Kraemer H, Stover E, Weinberger DR, Zalcman S, Marder SR (2004) Approaching a consensus cognitive battery for clinical trials in schizophrenia: the NIMH-MATRICS conference to select cognitive domains and test criteria. Biol Psychiatry 56:301–307
Heinrichs RW, Zakzanis KK (1998) Neurocognitive deficit in schizophrenia: a quantitative review of the evidence. Neuropsychology 12:426–445
Hoff AL, Harris D, Faustman WO, Beal M, DeVilliers D, Mone RD, Moses JA, Csernansky JG (1996) A neuropsychological study of early onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 20:21–28
Hollingshead A, Redlich F (1958) Social class and mental illness: a community study. Wiley, New York
Hollis C (2000) Adult outcomes of child- and adolescent-onset schizophrenia: diagnostic stability and predictive validity. Am J Psychiatry 157:1652–1659
Hollis C (2003) Child and adolescent onset schizophrenia. In: Hirsch SR, Weinberger D (eds) Schizophrenia. Blackwell, Malden, pp 34–53
Kenny JT, Friedman L, Findling RL, Swales TP, Strauss ME, Jesberger JA, Schulz SC (1997) Cognitive impairment in adolescents with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 154:1613–1615
Krabbendam L, Arts B, van Os J, Aleman A (2005) Cognitive functioning in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a quantitative review. Schizophr Res 80:137–149
Kravariti E, Morris RG, Rabe-Hesketh S, Murray RM, Frangou S (2003) The Maudsley early-onset schizophrenia study: cognitive function in adolescent-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 65:95–103
Kumra S, Wiggs E, Bedwell J, Smith AK, Arling E, Albus K, Hamburger SD, McKenna K, Jacobsen LK, Rapoport JL, Asarnow RF (2000) Neuropsychological deficits in pediatric patients with childhood-onset schizophrenia and psychotic disorder not otherwise specified. Schizophr Res 42:135–144
Lezak M (1995) Neuropsychological assessment. Oxford University Press, Nueva York
Mayoral M, Zabala A, Robles O, Bombin I, Andres P, Parellada M, Moreno D, Graell M, Medina O, Arango C (2008) Neuropsychological functioning in adolescents with first episode psychosis: a two-year follow-up study. Eur Psychiatry 23(5):375–383
McClellan J, Prezbindowski A, Breiger D, McCurry C (2004) Neuropsychological functioning in early onset psychotic disorders. Schizophr Res 68:21–26
Mohr F, Hubmann W, Albus M, Franz U, Hecht S, Scherer J, Binder J, Sobizack N (2003) Neurological soft signs and neuropsychological performance in patients with first episode schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 121:21–30
Oie M, Rund BR (1999) Neuropsychological deficits in adolescent-onset schizophrenia compared with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 156:1216–1222
Oie M, Rund BR, Sundet K, Bryhn G (1998) Auditory laterality and selective attention: normal performance in patients with early-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 24:643–652
Peralta V, Cuesta M (1994) Validación de la escala de los síndromes positivo y negativo (PANSS) en una muestra de esquizofrénicos españoles. Actas Luso- Esp Neurol Psiquiatr 22:171–177
Riley EM, McGovern D, Mockler D, Doku VC SOC, Fannon DG, Tennakoon L, Santamaria M, Soni W, Morris RG, Sharma T (2000) Neuropsychological functioning in first-episode psychosis—evidence of specific deficits. Schizophr Res 43:47–55
Rund BR, Zeiner P, Sundet K, Oie M, Bryhn G (1998) No vigilance deficit found in either young schizophrenic or ADHD subjects. Scand J Psychol 39:101–107
Schretlen DJ, Cascella NG, Meyer SM, Kingery LR, Testa SM, Munro CA, Pulver AE, Rivkin P, Rao VA, Diaz-Asper CM, Dickerson FB, Yolken RH, Pearlson GD (2007) Neuropsychological functioning in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 62(2):179–186
Strauss E, Spreen O, SEM S (2006) A compendium of neuropsychological tests: administration norms and commentary. Oxford University Press, New York
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Health, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, CIBERSAM; RETICS RD06/0011(REM-TAP Network) and G03/032 (The First-Episode Early-Onset Psychosis Network). Other support came from the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) (A. Zabala) and the Spanish Ministry of Health: Healthcare Research Grants PI02/1248 and PI05/0678 (Dr. Arango). The authors thank James Gold, PhD for comments on the manuscript and Jose de Arriba for data management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zabala, A., Rapado, M., Arango, C. et al. Neuropsychological functioning in early-onset first-episode psychosis: comparison of diagnostic subgroups. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 260, 225–233 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-009-0046-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-009-0046-9