Abstract
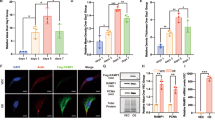
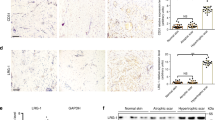
Skin fibroblasts modulate tissue repair, wound healing and immunological responses. Adrenergic receptors (ARs) mediate important physiological functions, such as endocrine, metabolic and neuronal activity. In this study, the expression α1A-ARs in human skin fibroblasts is examined and verified. Regulatory effects of α1-agonist cirazoline on cell migration and the production of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), hyaluronan (HA), fibronectin and procollagen type I carboxy-terminal peptide (PIP) by human skin fibroblasts are assessed and validated. α1A-AR mRNA and protein were found in human skin fibroblasts WS1. Exposure of cirazoline doubled skin fibroblast migration and the increase in cell migration was attenuated by α1-antagonist prazosin. TGF-β1 mRNA and production were enhanced after exposure to cirazoline and IGF-1 production was also increased after treatment with cirazoline. Exposure to cirazoline also enhanced HA and PIP production. The increases in TGF-β1, IGF-1, HA and PIP production were partially abolished in fibroblasts transfected with α1A-AR short interfering RNAs, indicating that α1A-ARs are involved in the cirazoline-induced increases in TGF-β1, IGF-1, HA and PIP production. Thus, α1A-ARs are stably expressed and stimulate cell migration and TGF-β1, IGF-1, HA and PIP production in human skin fibroblasts. Moreover, TGF-β1, IGF-1, HA and PIP production and the cell migration of human skin fibroblasts are possibly modulated by natural catecholamines produced by the endocrine system or sympathetic innervation, which could directly or indirectly participate in cytokine secretion, fibroblast migration and matrix production of wound healing in the skin.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai M, Nagasawa T, Koshihara Y, Yamamoto S, Togari A (2003) Effects of beta-adrenergic agonists on bone-resorbing activity in human osteoclast-like cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1640:137–142
Barth W, Deten A, Bauer M, Reinohs M, Leicht M, Zimmer HG (2000) Differential remodeling of the left and right heart after norepinephrine treatment in rats: studies on cytokines and collagen. J Mol Cell Cardiol 32:273–284
Briest W, Homagk L, Rassler B, Ziegelhoffer-Mihalovicova B, Meier H, Tannapfel A, Leiblein S, Saalbach A, Deten A, Zimmer HG (2004) Norepinephrine-induced changes in cardiac transforming growth factor-beta isoform expression pattern of female and male rats. Hypertension 44:410–418
Burger A, Benicke M, Deten A, Zimmer HG (2001) Catecholamines stimulate interleukin-6 synthesis in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H14–H21
Clark RA (1993) Biology of dermal wound repair. Dermatol Clin 11:647–666
Delella FK, Lacorte LM, Almeida FL, Pai MD, Felisbino SL (2012) Fibrosis-related gene expression in the prostate is modulated by doxazosin treatment. Life Sci 91:1281–1287
Ducy P, Schinke T, Karsenty G (2000) The osteoblast: a sophisticated fibroblast under central surveillance. Science 289:1501–1504
Faber JE, Yang N, Xin X (2001) Expression of alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes by smooth muscle cells and adventitial fibroblasts in rat aorta and in cell culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:441–452
Fisher GJ, Datta SC, Talwar HS, Wang ZQ, Varani J, Kang S, Voorhees JJ (1996) Molecular basis of sun-induced premature skin ageing and retinoid antagonism. Nature 379:335–339
Fisher GJ, Wang ZQ, Datta SC, Varani J, Kang S, Voorhees JJ (1997) Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. N Engl J Med 337:1419–1428
Freinkel RK, Woodley DT (2001) The biology of the skin. Parthenon, New York
Haase I, Evans R, Pofahl R, Watt FM (2003) Regulation of keratinocyte shape, migration and wound epithelialization by IGF-1- and EGF-dependent signalling pathways.J Cell Sci 116:3227-3238
Huang HH, Brennan TC, Muir MM, Mason RS (2009) Functional alpha1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors in human osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol 220:267–275
Ignotz RA, Massague J (1986) Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem 261:4337–4345
Khan AS, Sane DC, Wannenburg T, Sonntag WE (2002) Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-1 and the aging cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res 54:25–35
Kondo S (2000) The roles of cytokines in photoaging. J Dermatol Sci 23 (Suppl 1):S30–S36
Koshimizu TA, Tanoue A, Hirasawa A, Yamauchi J, Tsujimoto G (2003) Recent advances in alpha1-adrenoceptor pharmacology. Pharmacol Ther 98:235–244
Kovacs EJ (2001) Fibrogenic cytokines: the roles of immune mediators in the development of scar tissue. Immunol Today 12:17–23
Lai KB, Sanderson JE, Yu CM (2009) Suppression of collagen production in norepinephrine stimulated cardiac fibroblasts culture: differential effect of alpha and beta-adrenoreceptor antagonism. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 23:271–280
Laplante AF, Germain L, Auger FA, Moulin V (2001) Mechanisms of wound reepithelialization: hints from a tissue-engineered reconstructed skin to long-standing questions. FASEB J 15:2377–2389
Leen JL, Izzo A, Upadhyay C, Rowland KJ, Dubé PE, Gu S, Heximer SP, Rhodes CJ, Storm DR, Lund PK, Brubaker PL (2011) Mechanism of action of glucagon-like peptide-2 to increase IGF-I mRNA in intestinal subepithelial fibroblasts. Endocrinology 152:436–446
Leicht M, Briest W, Zimmer HG (2003) Regulation of norepinephrine-induced proliferation in cardiac fibroblasts by interleukin-6 and p42/p44 mitogen activated protein kinase. Mol Cell Biochem 243:65–72
Leicht M, Greipel N, Zimmer H (2000) Comitogenic effect of catecholamines on rat cardiac fibroblasts in culture. Cardiovasc Res 48:274–284
Lewis DA, Travers JB, Somani AK, Spandau DF (2010) The IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling axis in the skin: a new role for the dermis in aging-associated skin cancer. Oncogene 29:1475–1485
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative and the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Luther HP, Podlowski S, Schulze W, Morwinski R, Buchwalow I, Baumann G, Wallukat G (2001) Expression of alpha1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in heart cell culture. Mol Cell Biochem 224:69–79
Makrantonaki E, Vogel K, Fimmel S, Oeff M, Seltmann H, Zouboulis CC (2008) Interplay of IGF-I and 17beta-estradiol at age-specific levels in human sebocytes and fibroblasts in vitro. Exp Gerontol 43:939–946
Malloy BJ, Price DT, Price RR, Bienstock AM, Dole MK, Funk BL, Rudner XL, Richardson CD, Donatucci CF, Schwinn DA (1998) Alpha1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in human detrusor. J Urol 160:937–943
Marinucci L, Balloni S, Bodo M, Carinci F, Pezzetti F, Stabellini G, Conte C, Lumare E (2009) Patterns of some extracellular matrix gene expression are similar in cells from cleft lip-palate patients and in human palatal fibroblasts exposed to diazepam in culture. Toxicology 257:10–16
Michelotti GA, Price DT, Schwinn DA (2000) Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor regulation: basic science and clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther 88:281–309
Noda M, Vogel R (1989) Fibroblast growth factor enhances type beta 1 transforming growth factor gene expression in osteoblast-like cells. J Cell Biol 109:2529–2535
Ongioco RR, Richardson CD, Rudner XL, Stafford-Smith M, Schwinn DA (2000) Alpha2-adrenergic receptors in human dorsal root ganglia: predominance of alpha2b and alpha2c subtype mRNAs. Anesthesiology 92:968–976
Perez DM, Papay RS, Shi T (2009) Alpha1-adrenergic receptor stimulates interleukin-6 expression and secretion through both mRNA stability and transcriptional regulation: involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB. Mol Pharmacol 76:144–152
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pfeilschifter J, Laukhuf F, Müller-Beckmann B, Blum WF, Pfister T, Ziegler R (1995) Parathyroid hormone increases the concentration of insulin-like growth factor-I and transforming growth factor beta 1 in rat bone. J Clin Invest 96:767–774
Price DT, Lefkowitz RJ, Caron MG, Berkowitz D, Schwinn DA (1994) Localization of mRNA for three distinct alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in human tissues: implications for human alpha-adrenergic physiology. Mol Pharmacol 45:171–175
Pullar CE, Grahn JC, Liu W, Isseroff RR (2006) Beta2-adrenergic receptor activation delays wound healing. FASEB J 20:76–86
Pullar CE, Isseroff RR (2006) The beta 2-adrenergic receptor activates pro-migratory and pro-proliferative pathways in dermal fibroblasts via divergent mechanisms. J Cell Sci 119:592–602
Pullar CE, Le Provost GS, O'Leary AP, Evans SE, Baier BS, Isseroff RR (2012) Beta2AR antagonists and beta2AR gene deletion both promote skin wound repair processes. J Invest Dermatol 132:2076–2084
Rassler B, Marx G, Schierle K, Zimmer HG (2012) Catecholamines can induce pulmonary remodeling in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 30:1134–1147
Rizzino A (1988) Transforming growth factor-beta: multiple effects on cell differentiation and extracellular matrices. Dev Biol 130:411–422
Roberts AB, Sporn MB, Assoian RK, Smith JM, Roche NS, Wakefield LM, Heine UI, Liotta LA, Falanga V, Kehrl JH et al (1986) Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:4167–4171
Rolfe KJ, Irvine LM, Grobbelaar AO, Linge C (2007) Differential gene expression in response to transforming growth factor-beta1 by fetal and postnatal dermal fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen 15:897–906
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386
Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1988) Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature 332:217–219
Sterin-Borda L, Furlan C, Orman B, Borda E (2007) Differential regulation on human skin fibroblast by alpha1 adrenergic receptor subtypes. Biochem Pharmacol 74:1401–1412
Sullivan DE, Ferris M, Nguyen H, Abboud E, Brody AR (2009) TNF-alpha induces TGF-beta1 expression in lung fibroblasts at the transcriptional level via AP-1 activation. J Cell Mol Med 13:1866–1876
Sullivan DE, Ferris M, Pociask D, Brody AR (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces transforming growth factor-beta1 expression in lung fibroblasts through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 32:242–249
Taguchi K, Yang M, Goepel M, Michel MC (1998) Comparison of human alpha1-adrenoceptor subtype coupling to protein kinase C activation and related signalling pathways. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 357:100–110
Tiedemann K, Malmstrom A, Westergren-Thorsson G (1997) Cytokine regulation of proteoglycan production in fibroblasts: separate and synergistic effects. Matrix Biol 15:469–478
Werner S, Krieg T, Smola H (2007) Keratinocyte-fibroblast interactions in wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 127:998–1008
Zak R (1973) Cell proliferation during cardiac growth. Am J Cardiol 31:211–219
Zhang H, Faber JE (2001) Trophic effect of norepinephrine on arterial intima-media and adventitia is augmented by injury and mediated by different alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Circ Res 89:815–822
Acknowledgments
The authors express their appreciation to Dr. Yu-Kuei Chen, Ms Tsuei-Ling Shiu, Mr. Jen-Jie Lin, Prof. Wen-Ling Shih, Dr. Yi-Lun Tsai, Dr. Yu-Jen Wu and Dr. Zhi-Jiao Cheng from Meiho University and National Pingtung University of Science and Technology for their research support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was funded by grants (NSC-100-2320-B-276-001 and NSC-101-2320-B-276-001) from the National Science Council, Taiwan.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, MH., Liu, SS., Peng, IC. et al. The stimulatory effects of alpha1-adrenergic receptors on TGF-beta1, IGF-1 and hyaluronan production in human skin fibroblasts. Cell Tissue Res 357, 681–693 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1893-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1893-x