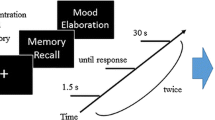
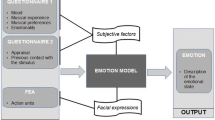
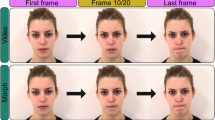
Abstract
The correspondence between facial expressions and emotions has been widely examined in psychology. However, studies have yet to record spontaneous facial expressions under well-controlled circumstances, thus the characteristics of these expressions remain unclear. Therefore, we compared the morphological and dynamic properties of spontaneous and posed facial expressions related to four different emotions: surprise, amusement, disgust, and sadness. First, we secretly recorded participants’ spontaneous facial expressions as they watched films chosen to elicit these four target emotions. We then recorded posed facial expressions of participants when asked to intentionally express each emotion. Subsequently, we conducted detailed analysis of both the spontaneous and posed expressions by using the Facial Action Coding System (FACS). We found different dynamic sequences between spontaneous and posed expressions for surprise and amusement. Moreover, we confirmed specific morphological aspects for disgust (the prevailing expressions of which encompassed other emotions) and posed negative emotions. This study provides new evidence of the characteristics for genuinely spontaneous and posed facial expressions corresponding to these emotions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bainum, C. K., Lounsbury, K. R., & Pollio, H. R. (1984). The development of laughing and smiling in nursery school children. Child Development, 1946–1957. doi:10.2307/1129941.
Barr, C. L., & Kleck, R. E. (1995). Self-other perception of the intensity of facial expressions of emotion: do we know what we show? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 68(4), 608–618. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.68.4.608.
Bonanno, G. A., & Keltner, D. (1997). Facial expressions of emotion and the course of conjugal bereavement. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 106(1), 126–137. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.106.1.126.
Buck, R., & VanLear, C. A. (2002). Verbal and nonverbal communication: distinguishing symbolic, spontaneous, and pseudo-spontaneous nonverbal behavior. Journal of Communication, 52(3), 522–541. doi:10.1111/j.1460-2466.2002.tb02560.x.
Carroll, J. M., & Russell, J. A. (1997). Facial expressions in Hollywood’s portrayal of emotion. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 72(1), 164–176. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.72.1.164.
Cohen, I., Sebe, N., Garg, A., Chen, L. S., & Huang, T. S. (2003). Facial expression recognition from video sequences: temporal and static modeling. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 91(1), 160–187. doi:10.1016/S1077-3142(03)00081-X.
Corneanu, C. A., Oliu, M., Cohn, J. F., & Escalera, S. (2016). Survey on RGB, 3D, thermal, and multimodal approaches for facial expression recognition: history, trends, and affect-related applications. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 99. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2515606.
Darwin, C. (1872). The expression of emotion in man and animals. New York: Oxford University Press.
Dimberg, U., Thunberg, M., & Elmehed, K. (2000). Unconscious facial reactions to emotional facial expressions. Psychological Science, 11(1), 86–89. doi:10.1111/1467-9280.00221.
Ekman, P. (1980). The face of man. New York: Garland Publishing, Inc..
Ekman, P. (1993). Facial expression and emotion. American Psychologist, 48(4), 384–392. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.48.4.384.
Ekman, P. (1994). All emotions are basic. In P. Ekman & R. J. Davidson (Eds.), The nature of emotion: Fundamental questions (pp. 15–19). New York: Oxford University Press.
Ekman, P. (2003). Emotions revealed. New York: Times Books.
Ekman, P., & Friesen, W. V. (1976). Pictures of facial affect. Palo Alto: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Ekman, P., & Friesen, W. V. (1978). Facial action coding system. Palo Alto: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Ekman, P., & Rosenberg, E. (2005). What the face reveals (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Ekman, P., Freisen, W. V., & Ancoli, S. (1980). Facial signs of emotional experience. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 39(6), 1125–1134. doi:10.1037/h0077722.
Ekman, P., Friesen, W. V., & Hager, J. C. (2002). Facial action coding system (2nd ed.). Salt Lake City: Research Nexus eBook.
Elfenbein, H. A., & Ambady, N. (2002). On the universality and cultural specificity of emotion recognition: a meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 128(2), 203–235. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.128.2.203.
Fernández-Dols, J. M., Sanchez, F., Carrera, P., & Ruiz-Belda, M. A. (1997). Are spontaneous expressions and emotions linked? An experimental test of coherence. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 21(3), 163–177. doi:10.1023/A:1024917530100.
Frank, M. G., Ekman, P., & Friesen, W. V. (1993). Behavioral markers and recognizability of the smile of enjoyment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 64(1), 83–93. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.64.1.83.
Galati, D., Sini, B., Schmidt, S., & Tinti, C. (2003). Spontaneous facial expressions in congenitally blind and sighted children aged 8-11. Journal of Visual Impairment and Blindness, 97(7), 418–428.
Gosselin, P., Kirouac, G., & Doré, F. Y. (1995). Components and recognition of facial expression in the communication of emotion by actors. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 68(1), 83–96. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.68.1.83.
Gross, J. J., & Levenson, R. W. (1995). Emotion elicitation using films. Cognition & Emotion, 9(1), 87–108. doi:10.1080/02699939508408966.
Hess, U., & Kleck, R. E. (1994). The cues decoders use in attempting to differentiate emotion-elicited and posed facial expressions. European Journal of Social Psychology, 24(3), 367–381. doi:10.1002/ejsp.2420240306.
Hess, U., & Kleck, R. (1997). Differentiating emotion elicited and deliberate emotional facial expressions. In P. Ekman & E. L. Rosenberg (Eds.), What the face reveals (2nd ed., pp. 271–288). New York: Oxford University Press.
Izard, C. E. (1977). Human emotions. New York: Plenum Press.
Jack, R. E., Garrod, O. G., & Schyns, P. G. (2014). Dynamic facial expressions of emotion transmit an evolving hierarchy of signals over time. Current Biology, 24(2), 187–192. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2013.11.064.
Johnston, L., Miles, L., & Macrae, C. N. (2010). Why are you smiling at me? Social functions of enjoyment and non-enjoyment smiles. British Journal of Social Psychology, 49(1), 107–127. doi:10.1348/014466609X412476.
Kaiser, S., & Wehrle, T. (2001). Facial expressions as indicators of appraisal processes. In K. R. Scherer, A. Schorr, & T. Johnstone (Eds.), Appraisal processes in emotion: Theory, methods, research(285–300). New York: Oxford University Press.
Kraft, T. L., & Pressman, S. D. (2012). Grin and bear it the influence of manipulated facial expression on the stress response. Psychological Science, 23(11), 1372–1378. doi:10.1177/0956797612445312.
Krumhuber, E. G., & Scherer, K. R. (2011). Affect bursts: dynamic patterns of facial expression. Emotion, 11(4), 825–841. doi:10.1037/a0023856.
Kunzmann, U., Kupperbusch, C. S., & Levenson, R. W. (2005). Behavioral inhibition and amplification during emotional arousal: a comparison of two age groups. Psychology and Aging, 20(1), 144–158. doi:10.1037/0882-7974.20.1.144.
Levenson, R. W., Ekman, P., Heider, K., & Friesen, W. V. (1992). Emotion and autonomic nervous system activity in the Minangkabau of west Sumatra. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 62(6), 972–988. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.62.6.972.
Matsumoto, D. (1992). American-Japanese cultural differences in the recognition of universal facial expressions. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 23(1), 72–84. doi:10.1177/0022022192231005.
Matsumoto, D., & Willingham, B. (2006). The thrill of victory and the agony of defeat: spontaneous expressions of medal winners of the 2004 Athens Olympic games. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 91(3), 568–581. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.91.3.568.
Matsumoto, D., & Willingham, B. (2009). Spontaneous facial expressions of emotion of congenitally and noncongenitally blind individuals. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 96(1), 1–10. doi:10.1037/a0014037.
Mauss, I. B., Levenson, R. W., McCarter, L., Wilhelm, F. H., & Gross, J. J. (2005). The tie that binds? Coherence among emotion experience, behavior, and physiology. Emotion, 5(2), 175–190. doi:10.1037/1528-3542.5.2.175.
Messinger, D. S., Mattson, W. I., Mahoor, M. H., & Cohn, J. F. (2012). The eyes have it: making positive expressions more positive and negative expressions more negative. Emotion, 12(3), 430–436. doi:10.1037/a0026498.
Mühlberger, A., Wieser, M. J., Gerdes, A. B., Frey, M. C., Weyers, P., & Pauli, P. (2011). Stop looking angry and smile, please: start and stop of the very same facial expression differentially activate threat- and reward-related brain networks. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 6(3), 321–329. doi:10.1093/scan/nsq039.
Reisenzein, R., Bördgen, S., Holtbernd, T., & Matz, D. (2006). Evidence for strong dissociation between emotion and facial displays: the case of surprise. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 91(2), 295–315. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.91.2.295.
Rosenberg, E. L., & Ekman, P. (1994). Coherence between expressive and experiential systems in emotion. Cognition & Emotion, 8(3), 201–229. doi:10.1080/02699939408408938.
Rozin, P., Haidt, J., & McCauley, C. R. (2008). Disgust. In M. Lewis, J. M. Haviland-Jones, & L. F. Barrett (Eds.), Handbook of emotions (3rd ed., pp. 757–776). New York: Guilford Press.
Russell, J. A. (1994). Is there universal recognition of emotion from facial expressions? A review of the cross-cultural studies. Psychological Bulletin, 115(1), 102–141. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.115.1.102.
Russell, J. A., Weiss, A., & Mendelsohn, G. A. (1989). Affect grid: a single-item scale of pleasure and arousal. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57(3), 493–502. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.57.3.493.
Sato, W., & Yoshikawa, S. (2007). Spontaneous facial mimicry in response to dynamic facial expressions. Cognition, 104(1), 1–18. doi:10.1016/j.cognition.2006.05.001.
Sato, W., Noguchi, M., & Yoshikawa, S. (2007). Emotion elicitation effect of films in a Japanese sample. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 35(7), 863–874. doi:10.2224/sbp.2007.35.7.863.
Scherer, K. R., & Ellgring, H. (2007). Are facial expressions of emotion produced by categorical affect programs or dynamically driven by appraisal? Emotion, 7(1), 113–130. doi:10.1037/1528-3542.7.1.113.
Schmidt, K. L., Ambadar, Z., Cohn, J. F., & Reed, L. I. (2006). Movement differences between deliberate and spontaneous facial expressions: Zygomaticus major action in smiling. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 30(1), 37–52. doi:10.1007/s10919-005-0003-x.
Susskind, J. M., Lee, D. H., Cusi, A., Feiman, R., Grabski, W., & Anderson, A. K. (2008). Expressing fear enhances sensory acquisition. Nature Neuroscience, 11(7), 843–850. doi:10.1038/nn.2138.
Takahashi, N., & Daibo, I. (2008). The results of researches on facial expressions of the Japanese: its issues and prospects. Institute of Electronics, Information, and Communication Engineers, 108(317), 9–10.
Tcherkassof, A., Bollon, T., Dubois, M., Pansu, P., & Adam, J. M. (2007). Facial expressions of emotions: a methodological contribution to the study of spontaneous and dynamic emotional faces. European Journal of Social Psychology, 37(6), 1325–1345. doi:10.1002/ejsp.427.
Van Der Schalk, J., Fischer, A., Doosje, B., Wigboldus, D., Hawk, S., Rotteveel, M., et al. (2011). Convergent and divergent responses to emotional displays of in-group and outgroup. Emotion, 11(2), 286–298. doi:10.1037/a0022582.
Vanhamme, J. (2003). Surprise … surprise. An empirical investigation on how surprise is connected to customer satisfaction (No. ERS-2003-005-MKT). ERIM Report Series Research in Management, Erasmus Research Institute of Management (ERIM). Retrieved from http://hdl.handle.net/1765/273 .
Wang, N., Marsella, S., & Hawkins, T. (2008). Individual differences in expressive response: a challenge for ECA design. Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Portugal, 3, 1289–1292.
Wehrle, T., Kaiser, S., Schmidt, S., & Scherer, K. R. (2000). Studying the dynamics of emotional expression using synthesized facial muscle movements. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78(1), 105–119. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.78.1.105.
Weiss, F., Blum, G. S., & Gleberman, L. (1987). Anatomically based measurement of facial expressions in simulated versus hypnotically induced affect. Motivation and Emotion, 11(1), 67–81. doi:10.1007/BF00992214.
Zeng, Z., Pantic, M., Roisman, G. I., & Huang, T. S. (2009). A survey of affect recognition methods: audio, visual, and spontaneous expressions. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 31(1), 39–58. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2008.52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This research was supported by the Center of Innovation Program of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) and by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grants 26285168 and 25870467.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedure performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the Ethical Committee of the Graduate School of Education, Hiroshima University.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants before and after the investigation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namba, S., Makihara, S., Kabir, R.S. et al. Spontaneous Facial Expressions Are Different from Posed Facial Expressions: Morphological Properties and Dynamic Sequences. Curr Psychol 36, 593–605 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-016-9448-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-016-9448-9